您现在的位置是:首页 >技术杂谈 >基于python使用Robust最小二乘法和RANSAC方法作直线拟合网站首页技术杂谈
基于python使用Robust最小二乘法和RANSAC方法作直线拟合
简介基于python使用Robust最小二乘法和RANSAC方法作直线拟合
一、原理
1.Robust最小二乘法(Robust Least Squares Method)
当数据中存在异常值时,最小二乘法的结果可能会受到较大的影响,导致模型的预测精度下降。为了增强对异常值的鲁棒性,Robust最小二乘法采用了不同的损失函数。传统的最小二乘法使用残差平方和作为损失函数,而Robust最小二乘法则使用对异常值不那么敏感的损失函数,如Huber损失、Tukey损失等。这些损失函数在残差较小时与残差平方和相似,但在残差较大时增长较慢,从而减小了异常值对参数估计的影响。
2.RANSAC方法(Random Sample Consensus,随机采样一致性)
RANSAC方法是一种基于随机采样的迭代算法,主要用于从包含大量噪声和异常值(外点)的数据集中估计数学模型参数。其从数据集中随机选择一组样本点(对于直线拟合,通常需要两个点来确定一条直线),再使用选择的样本点来估计直线模型的参数(斜率和截距),并计算数据集中剩余点到估计直线的距离,将距离小于某个阈值的点视为内点。统计内点的数量,并评估当前模型的质量(通常以内点数量作为评估标准)。重复步骤多次(通常预设一个最大迭代次数),每次迭代都会生成一个新的模型,并选择内点数量最多的模型作为当前最佳模型。当达到最大迭代次数或当前最佳模型的质量不再显著提高时,算法终止,并输出最终的最佳模型。
二、代码
1.Robust最小二乘法
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# robust最小二乘法函数
def robust_least_squares(x, y, degree, iterations, epsilon):
# 初始化参数
theta = np.zeros(degree + 1)
m = len(x)
# 添加偏置项(x^0 = 1)
X = np.column_stack([np.power(x, i) for i in range(degree + 1)])
# 迭代更新参数
for _ in range(iterations):
# 计算预测值
y_pred = np.dot(X, theta)
# 计算残差
residuals = y - y_pred
# 计算权重矩阵
weights = np.diag(1 / (np.abs(residuals) + epsilon))
# 更新参数(使用加权最小二乘法)
theta = np.linalg.inv(X.T @ weights @ X) @ X.T @ weights @ y
return theta
# 读取图像并处理
image = cv2.imread('dot.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 存储x和y坐标
x_coords = []
y_coords = []
# 遍历轮廓,找到每个点的中心
for contour in contours:
M = cv2.moments(contour)
if M["m00"] != 0:
cX = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"]) / 1000
cY = (600 - int(M["m01"] / M["m00"])) / 1000
x_coords.append(cX)
y_coords.append(cY)
X_data = np.array(x_coords)
y_data = np.array(y_coords)
# 设置多项式的度数、迭代次数和epsilon值
degree = 1 #多项式次数
iterations = 100 # 迭代次数
epsilon = 1e-6 # 避免除以零的小正数
# 使用函数拟合曲线并打印拟合参数
theta_optimal = robust_least_squares(X_data, y_data, degree, iterations, epsilon)
print("Optimal theta values:", theta_optimal)
# 生成用于绘图的x值范围
x_fit = np.linspace(min(X_data), max(X_data), 100).reshape(-1, 1)
# 使用拟合参数计算y值
y_fit = np.dot(np.column_stack([np.power(x_fit, i) for i in range(degree + 1)]), theta_optimal)
# 绘制样本点和拟合曲线
plt.scatter(X_data, y_data, label='数据点')
plt.plot(x_fit, y_fit, color='red', label='拟合曲线')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.legend()
plt.title('robust最小二乘法拟合')
plt.show()
2.RANSAC方法
import cv2
from copy import copy
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import default_rng
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
rng = default_rng()
# 定义RANSAC类,用于实现随机抽样一致性算法
class RANSAC:
def __init__(self, n=10, k=100, t=0.05, d=10, model=None, loss=None, metric=None):
# 初始化参数
self.n = n # 最小数据点数量,用于估计模型参数
self.k = k # 最大迭代次数
self.t = t # 阈值,用于确定点是否拟合良好
self.d = d # 所需接近数据点的数量,以确认模型拟合良好
self.model = model # 模型类,实现fit和predict方法
self.loss = loss # 损失函数,返回y_true和y_pred之间的向量
self.metric = metric # 度量函数,返回y_true和y_pred之间的浮点数
self.best_fit = None # 最佳拟合模型
self.best_error = np.inf # 最佳误差,初始化为无穷大
def fit(self, X, y):
# 对数据进行RANSAC拟合
for _ in range(self.k):
ids = rng.permutation(X.shape[0])# 对数据点进行随机排列
maybe_inliers = ids[: self.n]# 选择前n个点作为可能的内点
maybe_model = copy(self.model).fit(X[maybe_inliers], y[maybe_inliers])# 使用这些点拟合模型
# 计算剩余点的损失,并确定哪些点满足阈值条件
thresholded = (
self.loss(y[ids][self.n :], maybe_model.predict(X[ids][self.n :]))
< self.t
)
inlier_ids = ids[self.n :][np.flatnonzero(thresholded).flatten()]# 获取满足条件的内点索引
# 如果内点数量足够,则更新模型
if inlier_ids.size > self.d:
inlier_points = np.hstack([maybe_inliers, inlier_ids])# 合并可能的内点和实际的内点
better_model = copy(self.model).fit(X[inlier_points], y[inlier_points])# 使用所有内点重新拟合模型
this_error = self.metric(
y[inlier_points], better_model.predict(X[inlier_points])# 计算当前模型的误差
)
# 如果当前模型的误差更小,则更新最佳拟合模型和最佳误差
if this_error < self.best_error:
self.best_error = this_error
self.best_fit = maybe_model
return self
def predict(self, X):
return self.best_fit.predict(X) # 使用最佳拟合模型进行预测
# 定义损失函数和度量函数
def square_error_loss(y_true, y_pred):
return (y_true - y_pred) ** 2 # 计算平方误差损失
def mean_square_error(y_true, y_pred):
return np.sum(square_error_loss(y_true, y_pred)) / y_true.shape[0] # 计算均方误差
# 定义线性回归模型类
class LinearRegressor:
def __init__(self):
self.params = None
def fit(self, X: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray):
# 拟合线性回归模型
r, _ = X.shape
X = np.hstack([np.ones((r, 1)), X])
self.params = np.linalg.inv(X.T @ X) @ X.T @ y
return self
def predict(self, X: np.ndarray):
# 使用线性回归模型进行预测
r, _ = X.shape
X = np.hstack([np.ones((r, 1)), X])
return X @ self.params
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建RANSAC实例,使用线性回归模型和定义的损失函数、度量函数
regressor = RANSAC(model=LinearRegressor(), loss=square_error_loss, metric=mean_square_error)
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread('dot.png')
# 转换为灰度图像
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 应用二值化
_, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
# 找到轮廓(这里假设点是小而圆的,因此可以使用findContours)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 存储x和y坐标
x_coords = []
y_coords = []
# 遍历轮廓,找到每个点的中心
for contour in contours:
# 计算轮廓的矩
M = cv2.moments(contour)
if M["m00"] != 0:
# 使用矩来计算中心
cX = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"])/1000
cY = (600-int(M["m01"] / M["m00"]))/1000
x_coords.append(cX)
y_coords.append(cY)
# 将坐标转换为NumPy数组
X = np.array(x_coords).reshape(-1, 1) # 现在x是一个二维数组,每行一个x坐标
y = np.array(y_coords).reshape(-1, 1)
# 拟合模型
regressor.fit(X, y)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax.set_box_aspect(1)
plt.scatter(X, y, label='数据点')
line = np.linspace(-1, 1, num=100).reshape(-1, 1)
plt.plot(line, regressor.predict(line), c="peru", label='拟合曲线')
# 设置坐标轴范围
plt.xlim(0, 1)
plt.ylim(0, 1)
plt.legend()
plt.title('RANSAC方法拟合直线')
plt.show()三、效果
1.Robust最小二乘法
原图: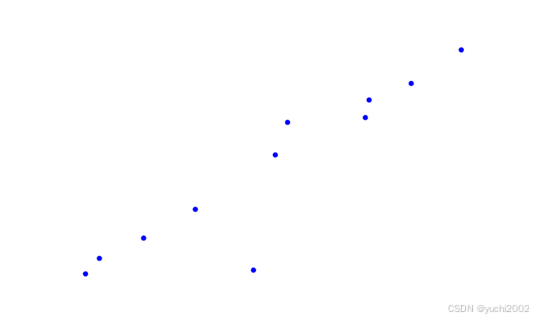
结果: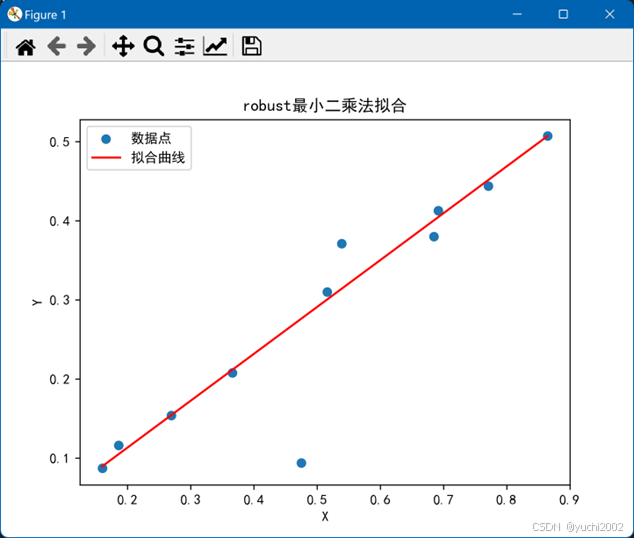
2.RANSAC方法
原图: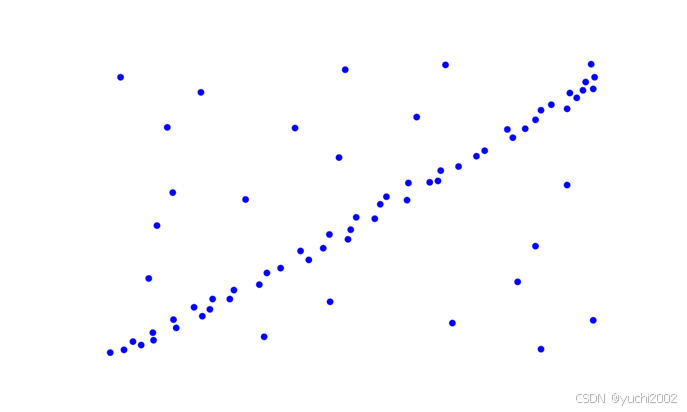
结果: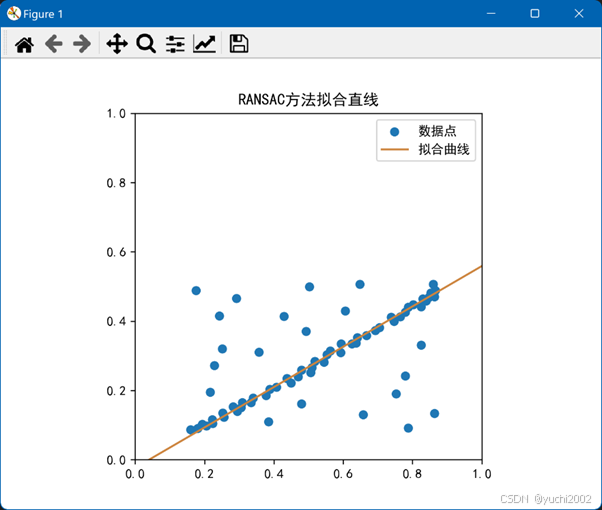
PS:画点函数
随手没有技术含量的画点函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 给定的坐标数据
X = np.array([-0.9,-0.83,-0.61,-0.35,-0.06,0.52,0.73,0.98,0.11,0.50,0.05]).reshape(-1, 1)
y = np.array([-0.93,-0.80,-0.63,-0.39,-0.9,0.53,0.67,0.95,0.34,0.38,0.07]).reshape(-1, 1)
# 创建图形和轴
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# 绘制散点图
plt.scatter(X, y, color='blue')#, label='Data Points'
# 添加标题和标签
# plt.title('Scatter Plot of X and y')
# plt.xlabel('X')
# plt.ylabel('y')
# plt.legend()
plt.axis('off')
# 保存图像到文件
plt.savefig('dot.png')
# 显示图形(可选,如果你想要立即看到图形)
# plt.show()风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结